Overview🔗
- 3D flow over a bump at a Reynolds number of \(10565\) (L=0.028m)
- Steady case used to initialise the transient case
- Steady case: simpleFoam
- Transient case: pimpleFoam
- Flow driven using a mean velocity force fvOption
- $FOAM_TUTORIALS/incompressible/pimpleFoam/LES/periodicHill
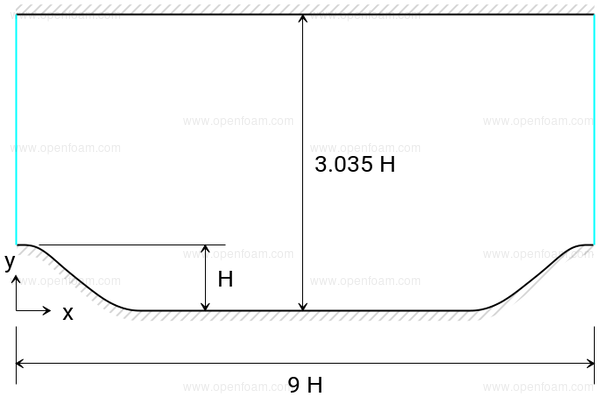
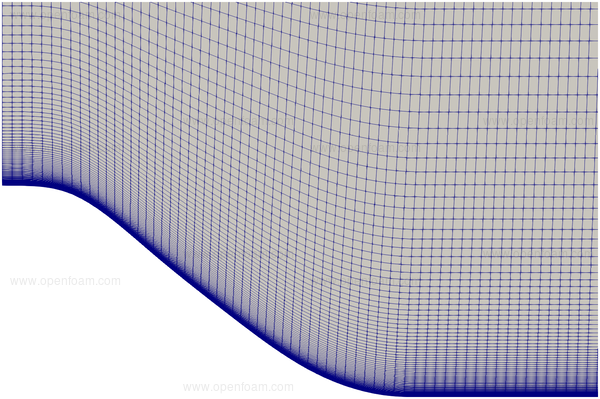
Mesh🔗
- 3D structured mesh created using blockMesh
-
hills described by the function
\[y(x) = \begin{cases} \min(1, a_1 + b_1 x + c_1 x^2 + d_1 x^3) & 0 \le x \lt 9, \\ a_2 + b_2 x + c_2 x^2 + d_2 x^3 & 9 \le x \lt 14, \\ a_3 + b_3 x + c_3 x^2 + d_3 x^3 & 14 \le x \lt 20, \\ a_4 + b_4 x + c_4 x^2 + d_4 x^3 & 20 \le x \lt 30, \\ a_5 + b_5 x + c_5 x^2 + d_5 x^3 & 30 \le x \lt 40, \\ \max(0, a_6 + b_6 x + c_6 x^2 + d_6 x^3) & 40 \le x \lt 54. \\ \end{cases}\]
| a | b | c | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | \(28\) | \(0\) | \(6.775070969851 \times 10^{-3}\) | \(- 2.124527775800 \times 10^{-3}\) |
| 2 | \(25.07355893131 \times 10^0\) | \(0.9754803562315 \times 10^{0}\) | \(- 1.016116352781 \times 10^{-1}\) | \(1.889794677828 \times 10^{-3}\) |
| 3 | \(2.579601052357 \times 10^1\) | \(8.206693007457 \times 10^{-1}\) | \(- 9.055370274339 \times 10^{-2}\) | \(1.626510569859 \times 10^{-3}\) |
| 4 | \(4.046435022819 \times 10^1\) | \(-1.379581654948 \times 10^{0}\) | \(1.945884504128 \times 10^{-2}\) | \(- 2.070318932190 \times 10^{-4}\) |
| 5 | \(1.792461334664 \times 10^1\) | \(8.743920332081 \times 10^{-1}\) | \(- 5.567361123058 \times 10^{-2}\) | \(6.277731764683 \times 10^{-4}\) |
| 6 | \(5.639011190988 \times 10^1\) | \(-2.010520359035 \times 10^{0}\) | \(1.644919857549 \times 10^{-2}\) | \(2.674976141766 \times 10^{-5}\) |
- this has been set in the
blockMeshDictusing acodeStream
Boundary conditions🔗
-
The mean bulk velocity \(\u_b\) at the inlet patch is defined as:
\[\u_b = \frac{1}{2.0355H}\int\limits_{H}^{3.035H} \u_x (y) dy\] - This is set to 1 m/s, and maintained using a mean velocity force fvOption
-
The laminar viscosity is set to achieve the target Reynolds numbers, where the reference length scale is given by the hill height
-
The laminar viscosity is derived from the Reynolds number, i.e.
\[\nu_\infty = \frac{|\u_b| H}{Re} = \frac{1 \times 0.028}{10565} = 2.65 \times 10^{-6} m^2/s\]
Common fields🔗
Velocity: U
Pressure: p
| Patch | Condition | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Inlet | cyclic | |
| Outlet | cyclic | |
| Hills | zeroGradient | |
| Walls | zeroGradient |
Turbulence fields🔗
- turbulence model: SA-IDDES
Turbulence viscosity: nut
| Patch | Condition | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Inlet | cyclic | |
| Outlet | cyclic | |
| Hills | nutUSpaldingWallFunction |
|
| Walls | nutUSpaldingWallFunction |
Spalart-Allmaras IDDES
Modified turbulence viscosity: nuTilda
| Patch | Condition | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Inlet | cyclic | |
| Outlet | cyclic | |
| Hills | fixedValue | 0 |
| Walls | fixedValue | 0 |
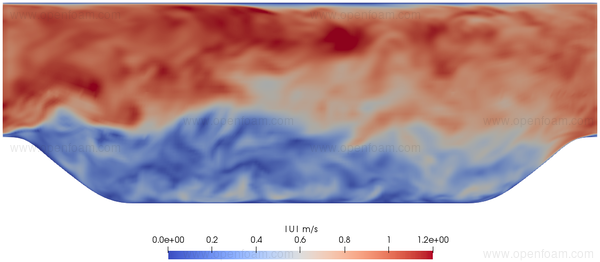
Results🔗
The precursor steady computation is used to initialise the transient calculation. After evolving the transient case for XXX flow-throughs a fully turbulent flow is established, as shown by the instantaneous velocity:
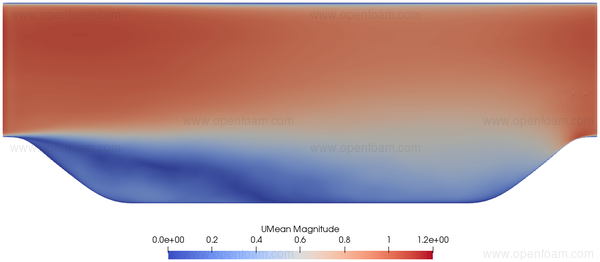
The average velocity prediction shows differences compared to the velocity derived from the precursor steady calculation:
Turbulent structures are clearly evident in the instantaneous Q criterion prediction:
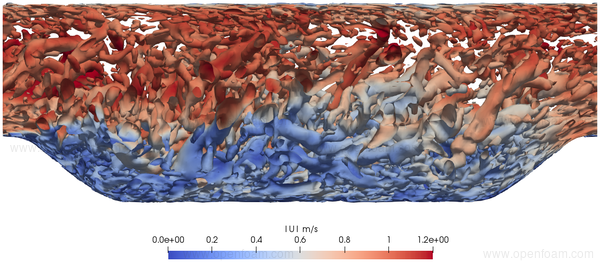
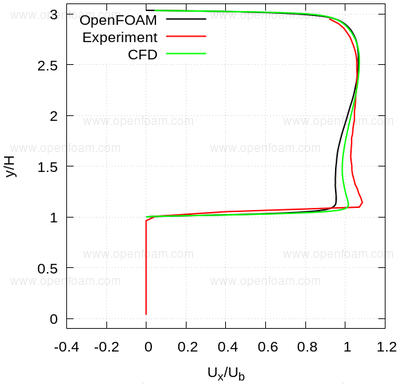
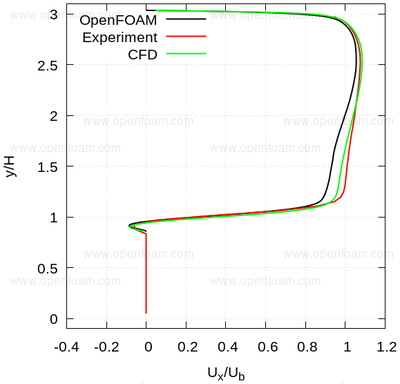
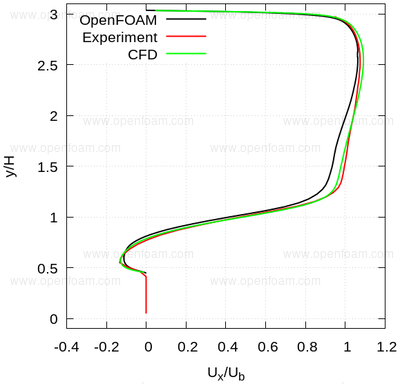
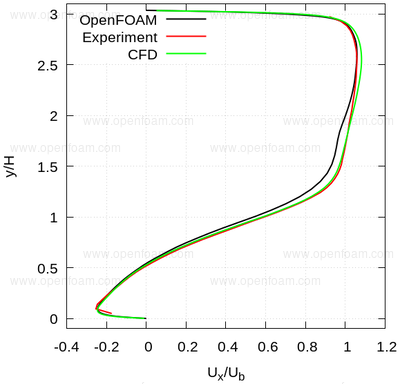
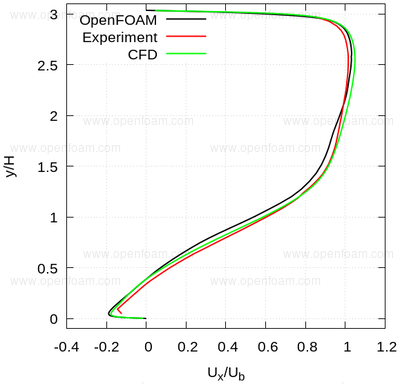
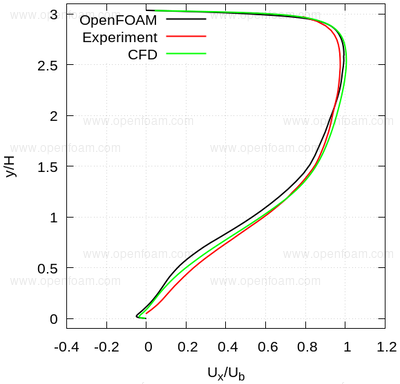
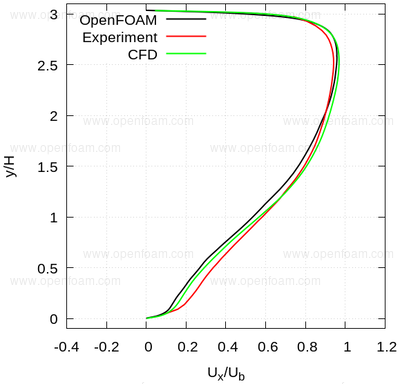
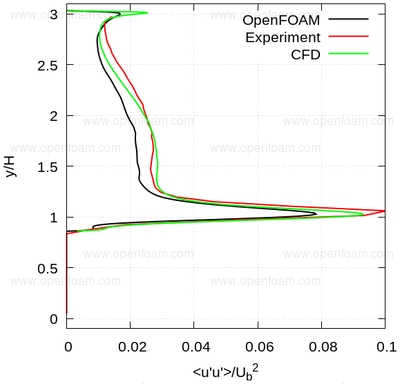
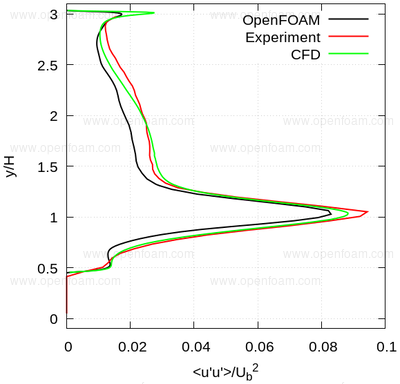
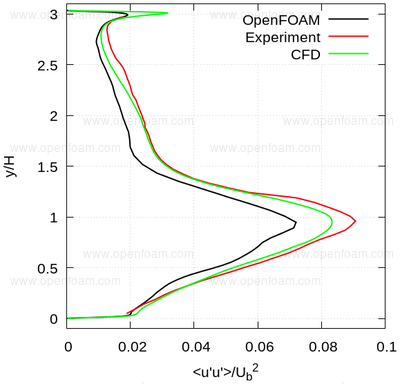
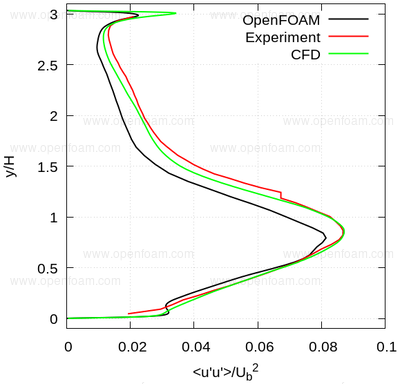
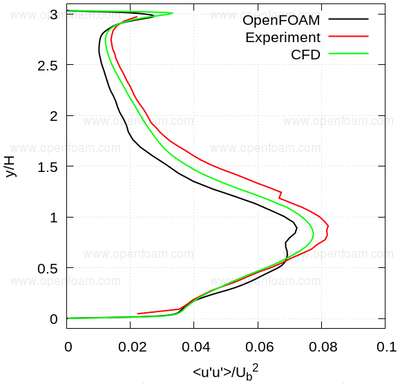
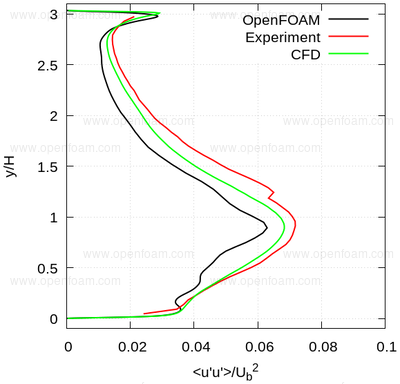
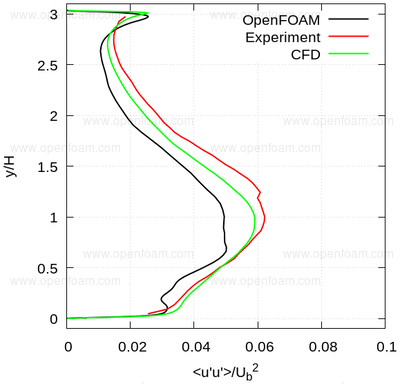
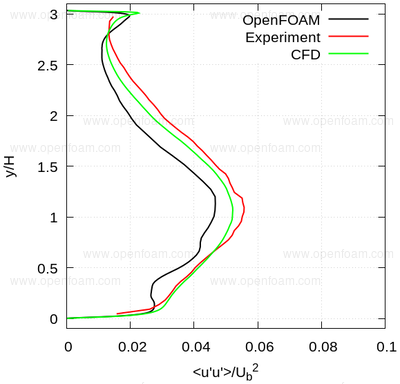
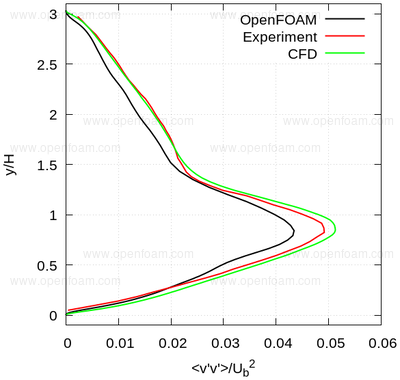
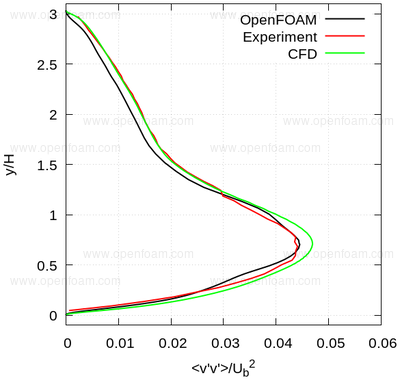
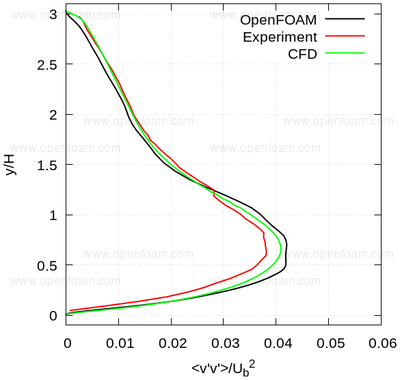
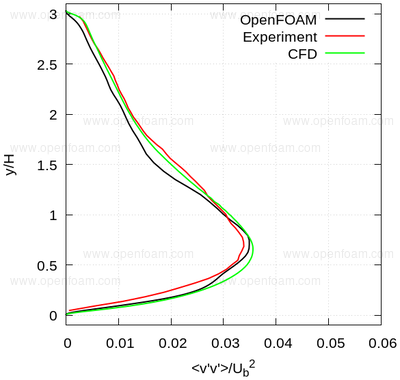
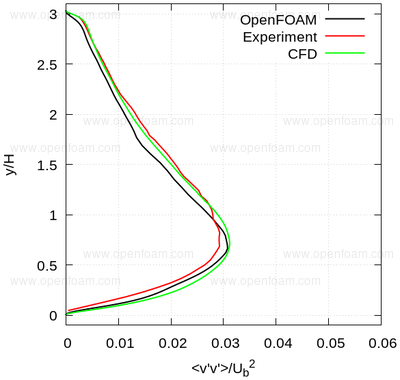
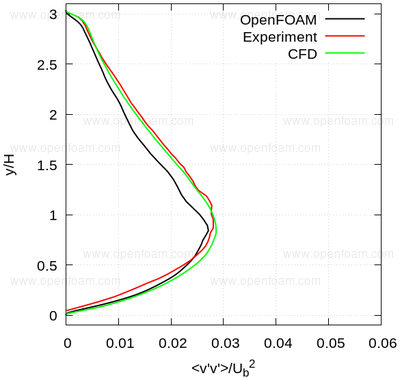
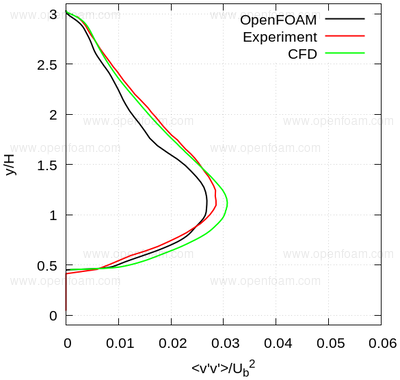
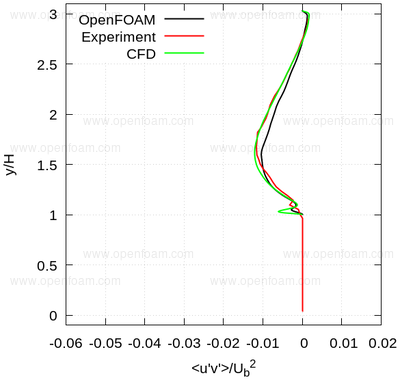
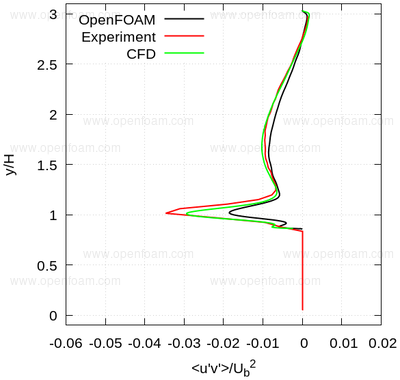
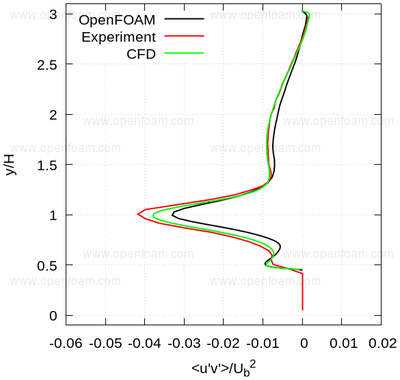
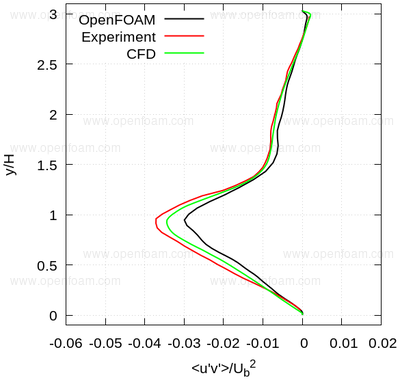
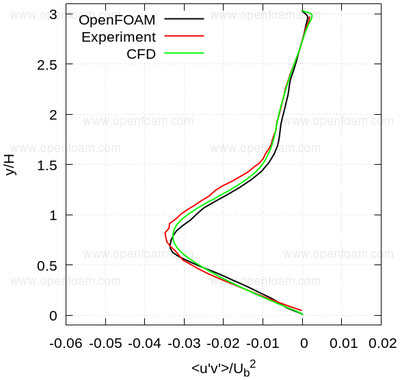
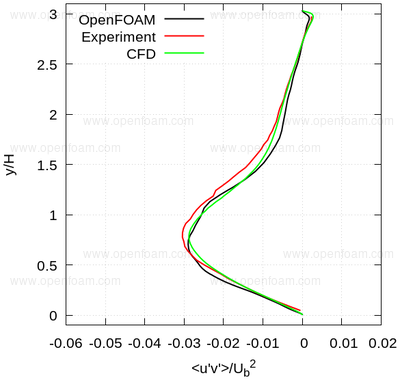
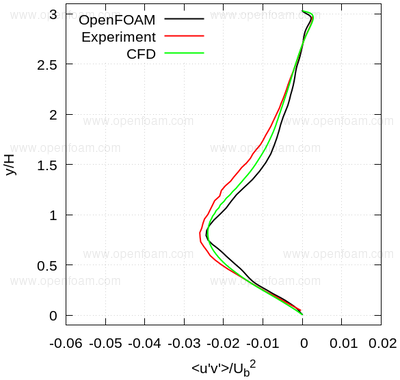
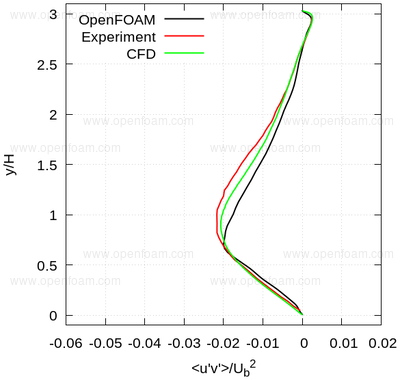
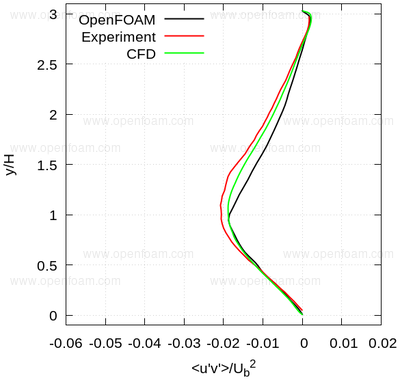
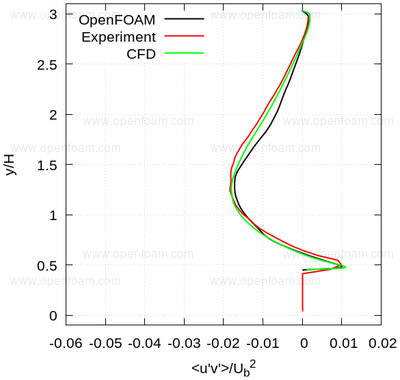
The following series of images provide a quantitative comparison between OpenFOAM predictions and both measured data and results from another CFD code at various streamwise locations.
Profiles🔗
Average velocity profiles:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
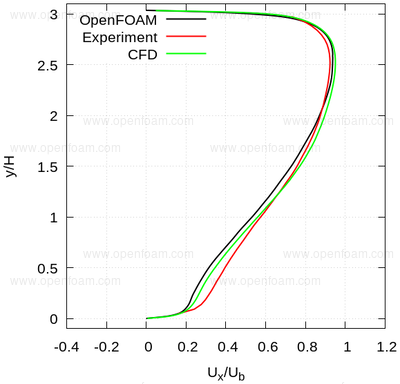 |
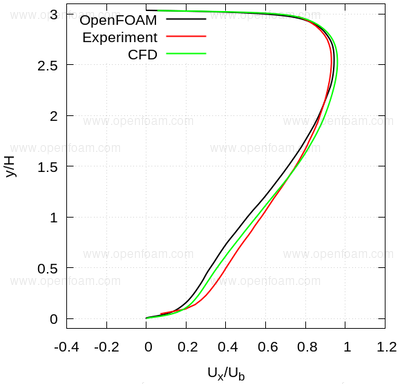 |
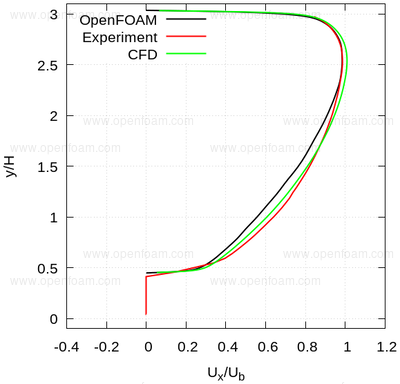 |
Average normal stresses: uu
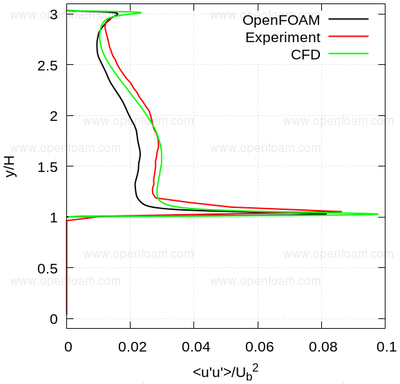 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
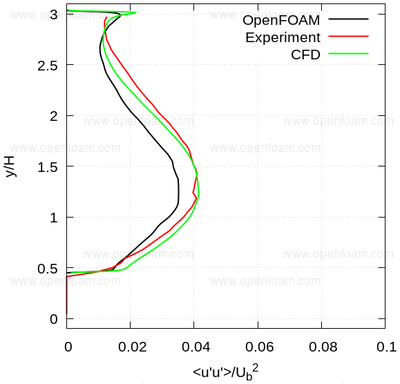 |
Average normal stresses: vv
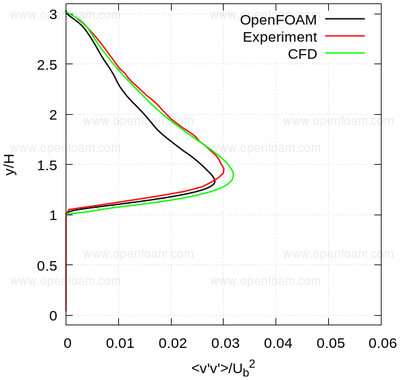 |
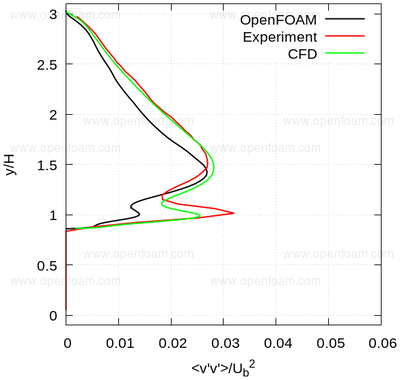 |
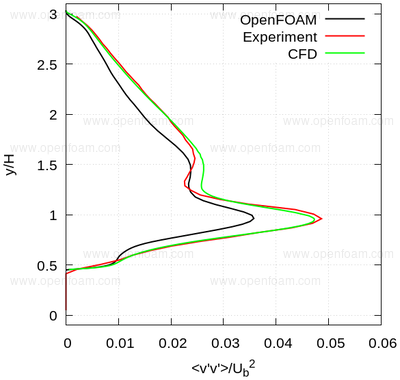 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Average shear stress: uv
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
